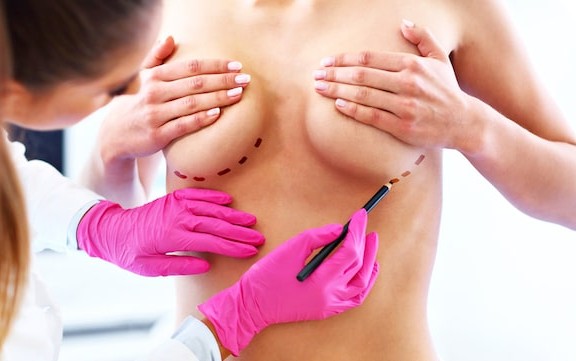
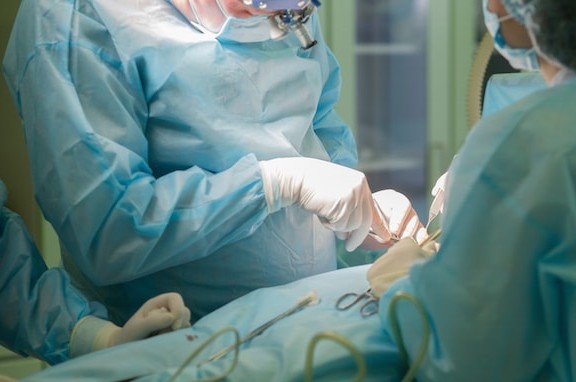
Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that is performed to rebuild a breast using prosthetics or tissue that comes from the body of the patient. Breast reconstruction is a popular choice for a patient who needed to have one or both breasts removed during a mastectomy. Breast reconstruction is also able to recreate the nipple and areola of the treated breast. Breast reconstruction works to restore the shape and size of the breasts to their pre-surgical state and increase the self-confidence of the patient.
Breast Reconstruction – Ideal Candidates
- Women who had one or both of their breasts removed
- Women who had breast cancer and have already undergone treatment for the condition
- Women who have undergone a lumpectomy
- Patients suffering from congenital deformities of the breasts
Breast Reconstruction – How it is Performed
Breast reconstruction can often be performed at the same time as breast cancer surgery while some patients wait until they have recovered from cancer surgery and/or cancer treatments. The reason some people wait is because chemotherapy and radiation therapy can impact the timing and the type of reconstruction treatment the patient might want.
The two most common types of breast reconstruction procedures are implant reconstruction and autologous tissue reconstruction or flap procedure:
- Implant reconstruction might require the patient to make multiple office visits over a period of several months to prepare the body for the implants. The surgeon can place a tissue expander in the breast area of the patient if there is not sufficient tissue on the chest wall to either cover or support an implant. An expandable balloon is placed and progressively filled, once a week, with salt water or air in order to form a breast mound. Once the breast tissue heals, the patient can have an additional procedure performed to replace the balloon with an implant.
- Autologous tissue reconstruction, AKA a flap procedure, uses the patient’s own blood vessels, fat, muscle, and skin to create a breast mound. During a TRAM flap, a flap of tissue is taken from the abdomen, and it can remain attached to the original blood supply while being tunneled up to the wall of the chest or it might be detached and reconnected to a new blood supply. The surgeon can also use other donor sites such as the thighs, back or buttocks. Alternative methods include DIEP flap and SIEA flap techniques where only skin and fat are transferred from the abdomen to the chest.
Nipple and areola reconstruction might be needed if they cannot be spared during a mastectomy. This is usually an additional surgery after breast reconstruction is completed. The procedure involves folding the skin to produce the shape of a nipple and tattooing the nipple for a realistic look and the illusion of projection.
Breast Reconstruction Recovery and Results
 The amount of recovery time needed on the part of the patient depends on the type of breast reconstruction being performed. Recovery from implant reconstruction is often quicker because the procedure is shorter while autologous tissue reconstruction has a longer surgical time and a longer recovery time.
The amount of recovery time needed on the part of the patient depends on the type of breast reconstruction being performed. Recovery from implant reconstruction is often quicker because the procedure is shorter while autologous tissue reconstruction has a longer surgical time and a longer recovery time.
Both types of breast reconstruction procedures require a short hospital stay. After implants, the patient is required to stay between 1 to 2 days while a flap procedure patient may be required to stay for 5 or 6 days. Gauze or bandages are applied to the incisions and small drainage tubes might be placed in the wound to remove excess fluid from the surgical site. A support garment is placed around the breasts to minimize swelling and support the breasts.
Patients can expect to feel tired and sore for a few weeks after either procedure. Bruising and swelling can last for up to 8 weeks. Patients should avoid any strenuous activity or exercise for the first 4 to 6 weeks. Normal activities can resume within 6 to 8 weeks. The surgeon will advise the patient when regular bras can be worn as well as any other suitable types of bras
Patients should know that reconstructed breasts will not have the same sensation as the replaced breast(s). Scarring may be present at the donor site for certain types of breast reconstruction, but they are often located in less exposed regions of the body such as the back, butt, or abdomen. It can take one to two years for the breast tissue to fully heal and for any scars to fade on the body. As time passes, the breast tissue can start to sag due to natural aging and gravity
Breast Reconstruction Risks
The risks involved with breast reconstruction can include:
- Bleeding issues or blood clots
- Infection
- Poor wound healing
- Seroma or fluid collection at the surgical site
- Uneven appearance to the breasts
- Loss of nipple sensation
- Capsular contracture
- Tightening of the breast or implant
For the best results, patients should consult with a board-certified plastic surgeon that is skilled in both types of breast reconstruction. A skilled surgeon who performs these procedures often will increase the odds of a successful procedure. During the consultation appointment, the surgeon will discuss all aspects of the surgery as well as the recovery process and any risks. The patient should also ask to see “before and after” photos of patients treated by the surgeon to help the patient understand what to expect after a breast reconstruction procedure.